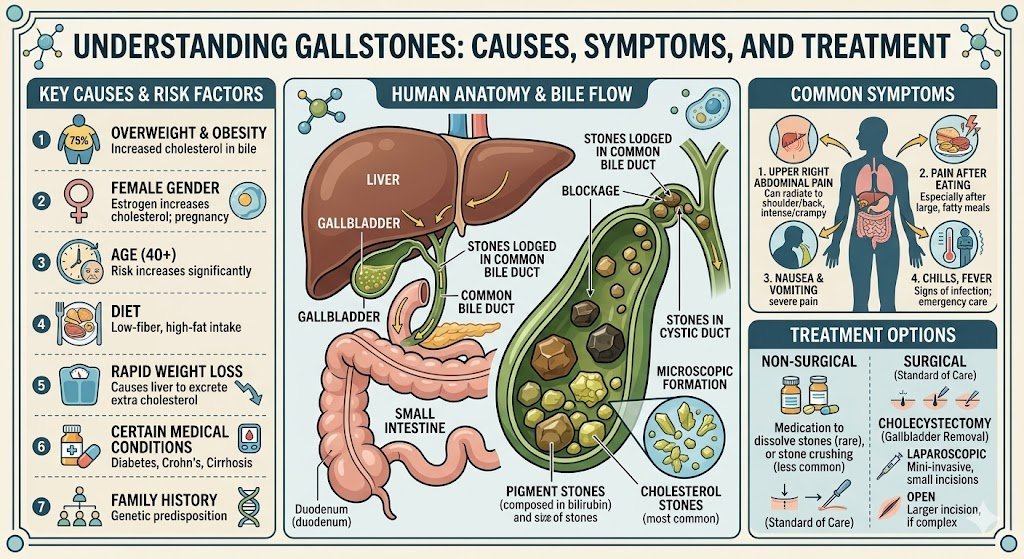
Solid particles called gallstones develop in the gallbladder, a little organ beneath the liver. They can cause serious health issues, such as discomfort and infection, and range in size from a grain of sand to a golf ball. Your gallbladder may develop hardened deposits of digestive fluid called gallstones. When the components of bile are out of balance, gallstones can form.
Types of Gallstones
Cholesterol Gallstones
The most prevalent kind of gallstones are cholesterol ones, which are mainly composed of undissolved cholesterol despite the fact that cholesterol is a natural part of bile.
Gallstones with Pigment
These stones are rarer and darker, composed of bilirubin. Those with certain medical diseases such as cirrhosis, biliary tract infections, or blood abnormalities like sickle cell anemia are typically the ones who experience them.
Causes of Gallstones
1. Composition of Bile
When bile has insufficient bile salts and excessive amounts of bilirubin or cholesterol, gallstones can develop. Stones are the result of bilirubin or cholesterol crystallizing due to this imbalance.
2. Urinary Tract Motility
Gallstones may form if the gallbladder does not empty entirely or frequently enough, causing the bile to become excessively concentrated.
Risk Factors
- Obesity: Carrying excess weight raises bile cholesterol levels, which can cause gallstones.
- Heavy-Fat Diet: Gallstones are more likely to occur in diets that are heavy in fat and cholesterol but poor in fiber.
- Quick Weight Loss: Excess cholesterol may be secreted into bile by the liver as a result of rapid weight loss.
- Age and Gender: Women and those over 40 are more vulnerable, especially if they are expecting, taking birth control pills, or using hormone replacement treatment.
- Family History: Gallstones may run in families, and genetics may be involved.
Symptoms of Gallstones
- Pain: Acute, quickly growing pain in your right shoulder, immediately behind your breastbone, or in the upper right section of your abdomen.
- Pain between your shoulder blades: Known as back pain.
- Vomiting and Nausea: Episodes frequently accompany pain.
Extreme Symptoms
- Fever and Chills: Indicate an infection.
- Jaundice: A yellowing of the skin and eyes that could indicate a bile duct obstruction.
- Severe Pain: Needing to be treated by a doctor right away and lasting more than a few hours.
Diagnosis
Physical Inspection
Physicians may feel for any abdominal pain, especially in the upper right quadrant, and may also search for fever or jaundice.
Imaging Examinations
- Ultrasound: The most used technique for locating gallstones. It can identify the existence of stones and project images of the gallbladder using sound waves.
- CT Scan: Yields fine-grained pictures of the bile ducts and gallbladder.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging: The bile ducts can be imaged to check for obstructions.
Alternative Diagnostic Techniques
- Blood Tests: May show indications of pancreatitis, infection, jaundice, or other gallstone-related problems.
- Hepatobiliary Iminodiacetic Acid (HIDA) Scan: Monitors the formation and movement of bile from your liver into your small intestine.
Complications of Gallstones
Acute Cholecystitis
Gallbladder inflammation, frequently brought on by gallstones obstructing the cystic duct. Severe pain, fever, and jaundice are among the symptoms.
Pancreatitis
Gallstones have the ability to obstruct the pancreatic duct, resulting in pancreatic inflammation. Severe stomach discomfort, nausea, and vomiting are some of the symptoms.
Cancer of the Gallbladder
Chronic gallstone disease can raise the chance of gallbladder cancer, however it is uncommon. The symptoms, which might include weight loss, jaundice, and stomach pain, are frequently identical to those of gallstones.
Treatment
Non-Surgical Interventions
- Medication: Ursodeoxycholic acid is a medication that dissolves cholesterol gallstones, however it can take months or years to work.
- Shock Wave Lithotripsy: Using sound waves, shock wave lithotripsy fragments gallstones into smaller fragments that can be passed through the bile ducts.
Surgical Procedures
- Cholecystectomy: The most popular therapy for symptomatic gallstones is cholecystectomy, which involves removing the gallbladder. This can be done through:
- Laparoscopic Surgery: A less intrusive method that requires less time to recuperate from.
- Open Surgery: Requires a longer recovery period and a larger incision.
Handling Symptoms
- Pain Management: Pain management options include prescription drugs and over-the-counter painkillers.
- Dietary Modifications: Reducing fat intake and eating fewer, but more frequent, meals can assist with symptoms.
Prevention of Gallstones
Dietary Suggestions
- Balanced Diet: One that is high in fiber and good fats and low in sugar and refined carbohydrates.
- Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight with diet and exercise.
Modifications in Lifestyle
- Frequent Exercise: Lowers the chance of gallstones.
- Steer Clear of Rapid Weight Decrease: Gallstones are less likely to occur with gradual weight decrease.
Strategies for Medical Prevention
- Medication: For people who are at a high risk of gallstones, like those who are losing weight quickly.
Living with Gallstones
Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications
- Healthy Eating: Increase your intake of whole grains, fruits, and veggies.
Monitoring and Following Care
- Regular Check-Ups: To keep an eye out for any possible issues.
- Self-Observation: Be mindful of your symptoms, and if things get worse, get help from a doctor.
Conclusion
Solid deposits called gallstones can lead to major health problems like discomfort and infection in the gallbladder. They mostly consist of bilirubin or cholesterol. Early diagnosis and treatment of gallstones depend on an understanding of the forms, causes, symptoms, and risk factors of the condition. Gallstones can be identified with the use of several diagnostic techniques, such as blood tests and ultrasounds. Medication, non-surgical techniques, and surgical gallbladder removal are among the available treatment options. Gallstones can be prevented with preventive measures such as a balanced diet, frequent exercise, and steady weight loss. To manage gallstones and avoid problems, lifestyle changes and monitoring are essential.